Check Running Processes Linux
Table of Contents
Introduction
Checking running processes in Linux is a common task that can be done using several tools and commands. Below are some of the most commonly used methods:
Using ps Command
The ps command provides information about currently running processes.
1
ps aux
a: Shows processes for all users.u: Displays a full-format listing.x: Includes processes not attached to a terminal.
Sample output
1
2
3
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.1 0.0 4588 3712 pts/0 Ss 19:31 0:00 bash
root 10 100 0.0 7888 3840 pts/0 R+ 19:31 0:00 ps aux
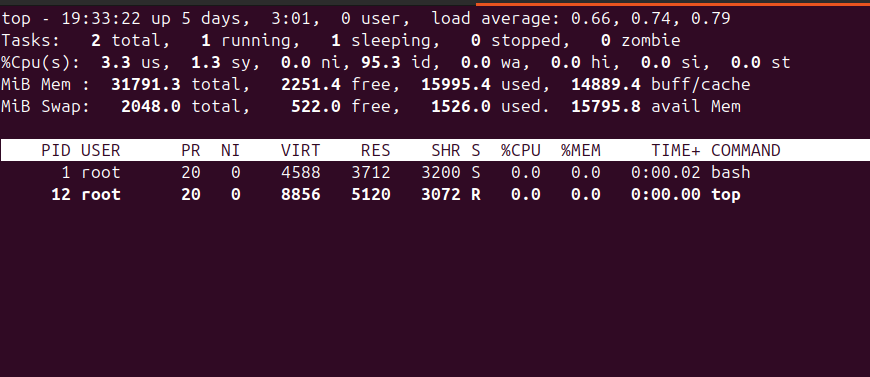
Using top Command
The top command is an interactive tool that displays real-time information about running processes.
1
top
This command provides a dynamic view of your system, showing you the most resource-intensive processes at the top. Press q to exit the top command.
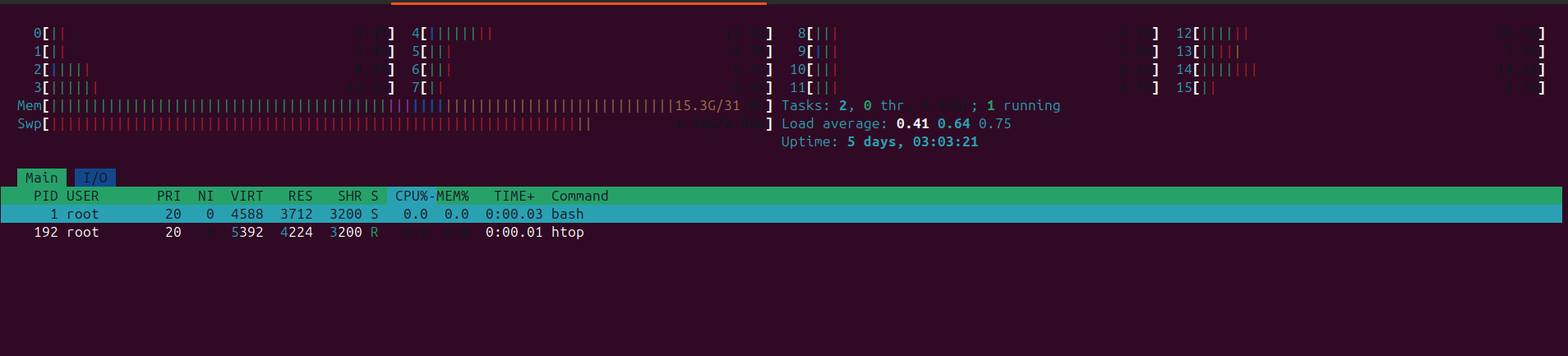
Using htop Command
The htop command is an enhanced version of top with a more user-friendly interface. It’s not pre-installed on all systems but can be easily installed using your package manager.
Debian/Ubuntu:
1
sudo apt-get install htop
Fedora:
1
sudo dnf install htop
Arch Linux:
1
sudo pacman -S htop
Once installed, you can run htop with:
1
htop
Using pidof Command
The pidof command is used to find the process ID(s) of a given process name.
1
pidof <process_name>
For example, to find the PID of the nginx process:
1
pidof nginx
Using pgrep Command
The pgrep command allows you to search for processes based on various attributes like name, user, or command line arguments.
1
pgrep <process_name>
For example, to find the PID of all ssh processes:
1
pgrep sshd
Using pkill Command
The pkill command is used to send signals to processes based on their names or attributes.
1
pkill <process_name>
For example, to kill all nginx processes:
1
pkill nginx
These commands and tools should help you effectively check and manage the running processes on your Linux system.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you should be able to free up significant space on your Linux system.